What Are Georgia’s Car Seat Laws?
Georgia has specific laws that require certain car safety seats for children. Children’s lives are precious, priceless and irreplaceable, so of course you want to protect them in every way you can. One of the ways that you can ensure your child’s safety is by utilizing the proper car seat every time you put them in a vehicle. However, it can be tricky to know what car seat your child needs. Today we will discuss what Georgia law tells us about your child’s car seat needs. Georgia has a statute, O.C.G.A. 40-8-76, which lays out child safety seat requirements. Georgia’s Car Seat Safety Statute is a primary law rather than a secondary law, meaning that you can be pulled over and cited for a violation, even if you have not committed another traffic violation.
Where Should My Child Be Seated in The Car?
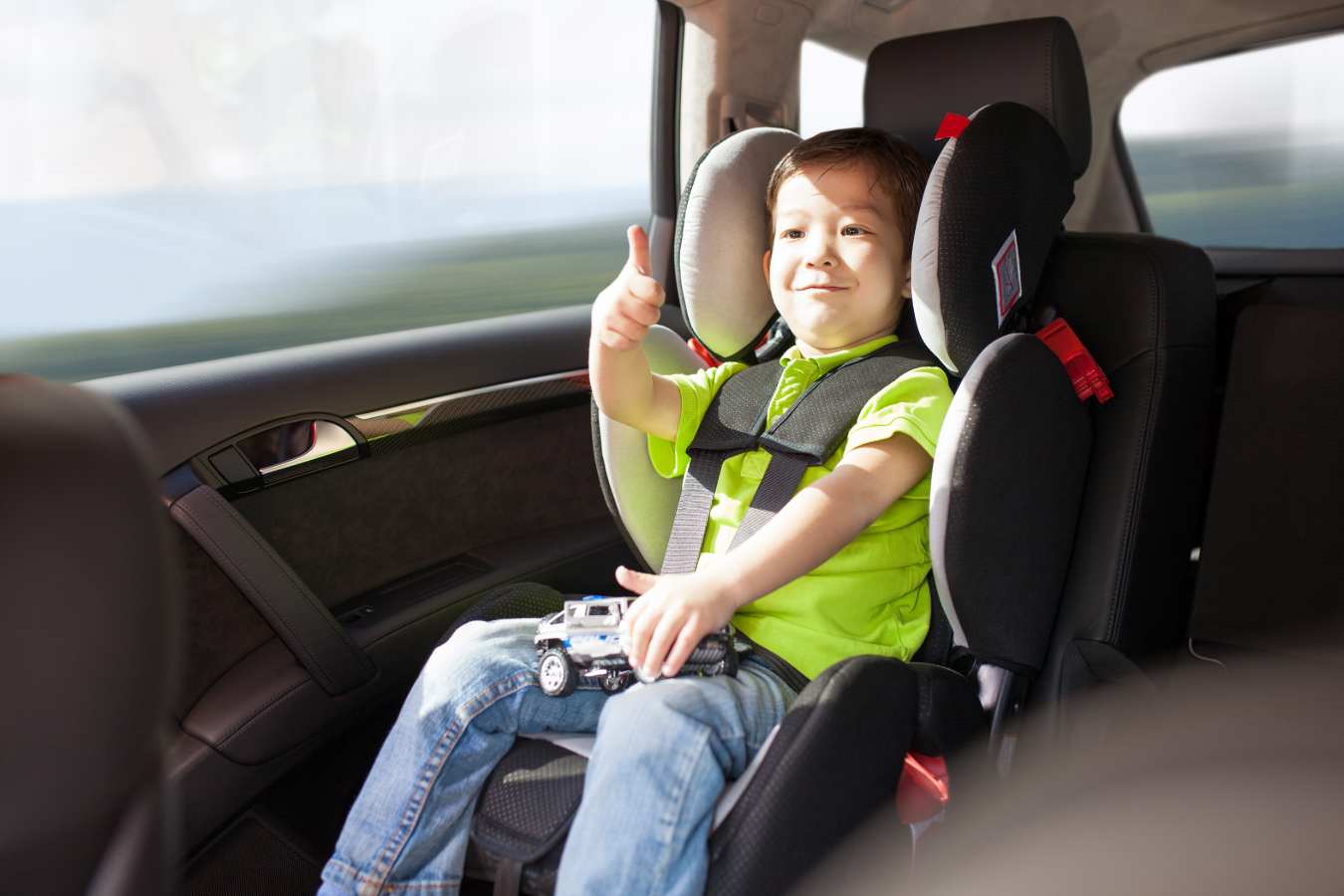
First and foremost, children under the age of 8 should always be in the back seat as required by Georgia law. It is recommended that children under the age of 13 ride in the back seat. All children under the age of 8 must be seated in the back seat in a proper safety seat based on their age, height and weight. Motor vehicle crashes are the number 1 cause of death of children in the US age 14 and under. Children seated in the front have a 40% to 70% higher risk of injury or death than children seated in the back. The linked study indicates that the center rear seat is the safest, with a risk reduction of 9%-24%. The reason that the center rear seat is the safest is because it is the position in the vehicle where the passenger is least likely to suffer an airbag injury or fatality. Children in the front seat are more likely to suffer injury or death caused by airbag deployment.
Which Car Seat is Right for My Child According to the Law?
Every child is different and Georgia laws account for that. Let’s look at age, weight and height requirements for child safety seats.
Georgia Law on Car Seats for Newborns and Infants:
You want to make sure your infant is protected in a rear-facing car seat until they are over the age of one year AND over 20 pounds. If your one-year-old is not yet 20 pounds, keep them in a rear-facing seat at least until they reach that milestone. It is recommended to keep your child rear-facing as long as possible. Even if your child is over 20 pounds, you may keep them in a rear-facing seat as long as that seat is rated for their weight and height per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Rear facing seats have harness-type straps that go over the head and should fit snuggly across the shoulders and chest. Some of these rear facing seats are designed to be rear facing only, while others are convertible models that can be adjusted to suit your child’s needs as they grow. Rear facing only seats usually come with a base that stays in the car, and the seat itself clicks onto the base. This makes it easier to transport your child to and from the car and also helps to ensure that the seat stays properly installed in your vehicle.
Georgia Law on Car Seats for Toddlers (One to Three Years):
Once your infant has reached one year AND 20 pounds, you can then transition them to a forward-facing car seat with a harness if you choose to do so. Just like the rear-facing seats, these front facing seats have harness-type straps that go over the head and should fit snuggly across the shoulders and chest. Your child should remain in a forward-facing seat with a harness until they are at least four years old AND over 40 pounds. Again, safety is our number one priority, so even if your child is over the age of four and over 40 pounds, you may choose to keep them restrained by a harness in a rear or front facing seat so long as the seat is rated for their weight and height per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Georgia Car Seat Laws for Young Children (Four to Eight Years):
Finally, your child is ready to graduate into a big kid booster seat! This means they have reached age four and are over 40 pounds. Your child should remain in a booster seat until they have reached the height of 4’9”. Children using booster seats are 59% less likely to be injured in a crash than those using a seatbelt alone, per the Georgia Department of Highway Safety. In this age range, children should remain in the back seat.
Children under 4’9” cannot safely sit in a car’s seat with the seatbelt alone, because the seatbelt will not fit them properly. The purpose of the booster seat is to position the child and the seatbelt so that your child is properly secured. Some of these seats have high backs, while some of them are backless. High-back booster seats are for smaller children, while the backless seats are for taller children.
Eight to Eighteen Years:
Once your child has reached the height of 4’9”, they may graduate from the booster to a regular car seat with seatbelt. Once your child reaches the age of 8, he or she may ride in the front seat, with either a booster, or without once they meet the height requirement. It is important that the seatbelt fit the child properly. The lap belt should sit snugly across the upper thighs (not the stomach), and the shoulder belt should rest snugly across the chest (not the neck or face). Your child should be tall enough to sit in the seat with their back to the seat and their knees bent over the edge of the seat comfortably. Your child needs to be able to maintain this seat position throughout the entirety of your trip, otherwise, they need to remain in a safety seat.
How Can I Be Sure My Child’s Safety Seat is Properly Installed?
According to a 2002 study, 81 percent of children are incorrectly restrained when traveling in a vehicle. In Georgia, you can go to your local fire department or any of the other locations linked below to learn how to properly install a car seat.
Georgia Department of Highway Safety’s list of Child Safety Seat Fitting Locations.
A Child Passenger Safety Technician (CPST) can also help you properly install your child’s car seat.
Child Safety Seat Tips:
- When the child is seated in a seat with a harness, the retainer clip at the top of the harness should sit at armpit level.
- Harness straps should be flat and untwisted and should be adjusted snugly.
- Lap belts should be fitted low and snugly across the hips.
- Shoulder belts should not sit across the face or neck, and should never be behind the child’s arms or back.
- Make sure your child’s safety seat is correctly rated for their height and weight per the manufacturer’s instructions. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your child’s safety seat.
- Do not use a secondhand safety seat or a seat that has been in a collision or has been recalled. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration has a tool that allows you to search and see if your child’s seat has been recalled. It is also important to register your car seat! Complete the registration that comes with your child’s car seat to receive notifications if the seat is ever recalled.
- Your child should not wear a large or puffy coat when in a safety seat, as this can prevent proper fitting of the harness, shoulder or lab belts. We’ve included a link to some tips to help keep your child warm and safe in the winter months while on the road.
- Car seats should be used for travel only. Do not allow your child to remain strapped into a car seat outside of the vehicle. This practice has resulted in unfortunate infant deaths. Car seats are not a replacement for cribs or bassinets.
- Do not use a seat that is too old, or has any visible damage, such as cracks or missing parts.
- Be a role model! Always wear your seatbelt (It’s the law, after all!) and help your child build the healthy habit of always buckling their seat belt when on the road. Remember, click it or ticket!
- Never leave your child unattended in or around a vehicle.
Your child’s safety is your highest priority as a parent. Ensuring that they are properly restrained every time you drive is the best way to keep your kids safe on the road. We have linked a recent Car Safety Seat Product Listing to help you choose the seat that is right for your child. For more child passenger safety information, please visit the Georgia Governor’s Office of Highway Safety website.